The Ultimate Guide to Energy-Efficient Windows: Choosing the Right Options for Your Home
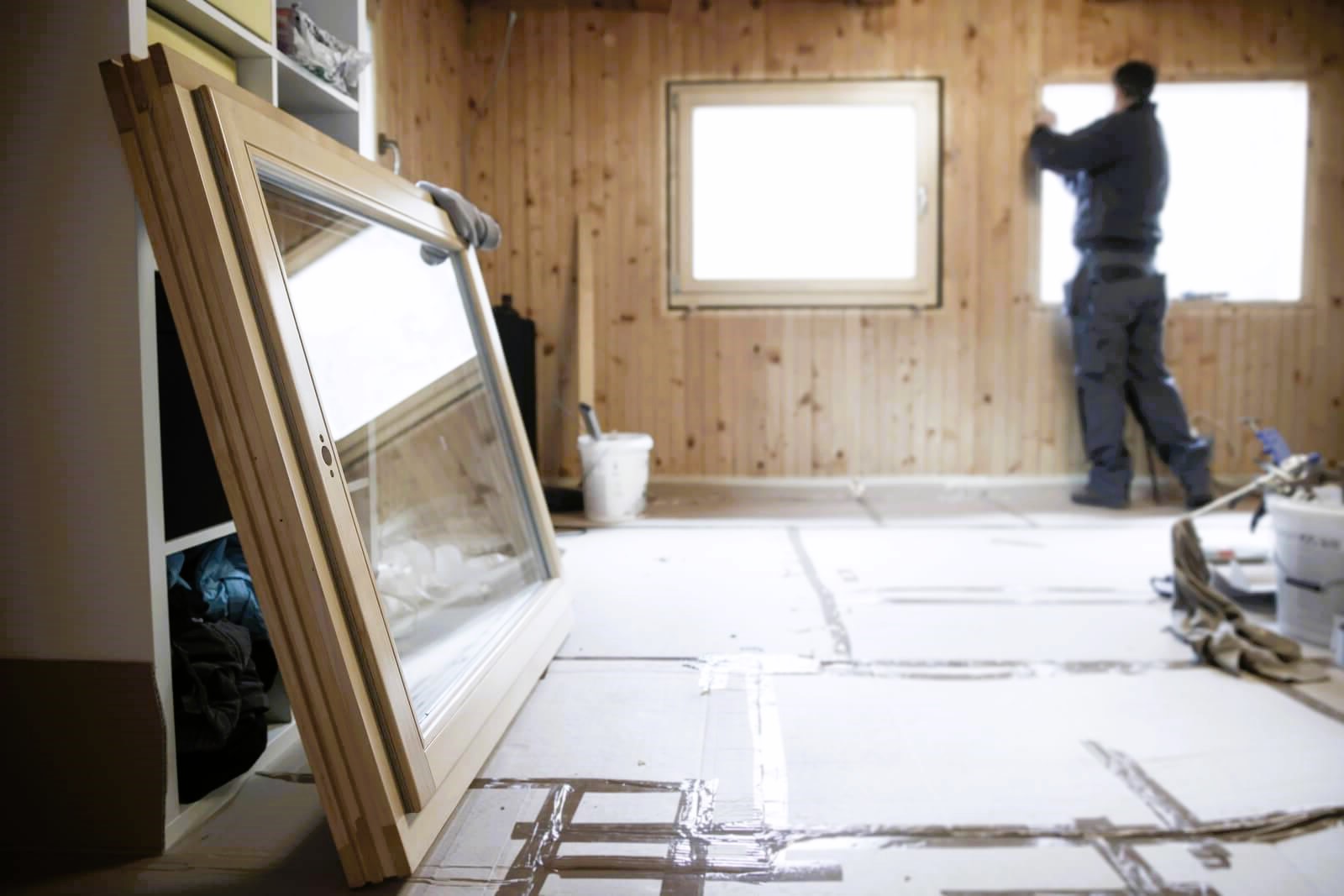
When it comes to making your home more energy-efficient, the choice of windows plays a crucial role. Energy-efficient windows not only contribute to reducing your carbon footprint but also offer substantial savings on your energy bills. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about energy-efficient windows, from their benefits to the various options available in the market.
Understanding Energy-Efficient Windows
Energy-efficient windows are designed to minimize heat transfer between the interior and exterior of your home. This is achieved through advanced technologies and innovative materials that enhance insulation and reduce the reliance on heating and cooling systems. The key features of energy-efficient windows include low-emissivity coatings, multiple panes, gas fills, and thermal breaks.
Benefits of Energy-Efficient Windows
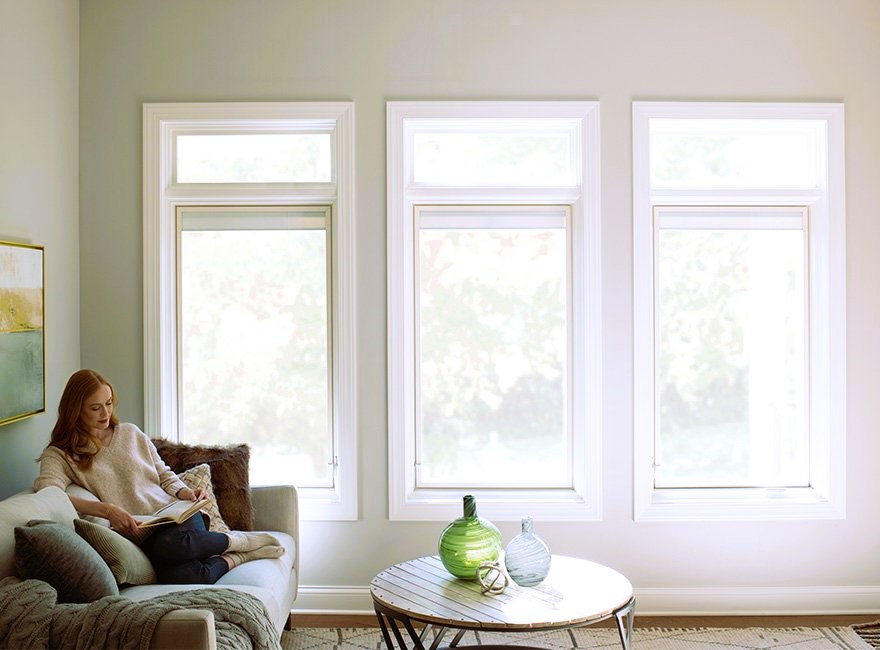

- Reduced Energy Consumption: Energy-efficient windows help in maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature, reducing the need for heating and cooling systems.
- Lower Utility Bills: By minimizing heat transfer, these windows lead to significant savings on your energy bills, making them a cost-effective investment.
- Environmental Impact: Using less energy translates to a smaller carbon footprint, contributing to environmental sustainability.
- Enhanced Comfort: Energy-efficient windows contribute to more consistent indoor temperatures, eliminating cold drafts and reducing noise infiltration.
Types of Energy-Efficient Windows
1. Double-Pane Windows
Double-pane windows consist of two layers of glass separated by a gas-filled space. This design enhances insulation and reduces heat transfer.
2. Triple-Pane Windows
Similar to double-pane windows, triple-pane windows have an additional layer of glass, providing even better insulation and energy efficiency.
3. Low-Emissivity (Low-E) Coatings
Low-E coatings are thin, virtually invisible layers applied to the glass surface to reflect infrared heat while allowing visible light to pass through.
4. Gas-Filled Windows
Argon or krypton gas can be filled between the window panes to provide additional insulation, reducing heat transfer.
5. Frame Materials
Choose frames made from energy-efficient materials such as vinyl, fiberglass, or wood clad with vinyl or aluminum to enhance overall window performance.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Energy-Efficient Windows
1. Climate Zone
Different window features are more effective in specific climate zones. Understanding your region’s climate helps in selecting windows that offer optimal performance. Innovative Trends in Modern Construction: What You Need to Know.
2. U-Factor and Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC)
These ratings indicate a window’s insulation and heat-blocking capabilities. Lower U-factor and SHGC values signify better energy efficiency.
3. Window Orientation
Consider the direction your windows face. Properly selected windows based on orientation can maximize natural light and minimize heat gain or loss.
4. Budget Considerations
While energy-efficient windows provide long-term savings, it’s essential to consider your budget and weigh the initial investment against the expected returns.
Installation and Maintenance Tips

- Professional Installation: Ensure that your energy-efficient windows are installed by certified professionals to guarantee proper fitting and performance.
- Regular Maintenance: Keep windows clean and check for any signs of wear, such as damaged seals or frames, to maintain optimal energy efficiency.
Conclusion
Investing in energy-efficient windows is a wise decision for homeowners looking to improve comfort, save on energy costs, and contribute to a greener environment. By understanding the various types of energy-efficient windows and considering key factors in the selection process, you can make informed choices that align with your home’s specific needs.
For more information on energy-efficient standards and guidelines in Canada, visit Wikipedia.